A large amount of work of the assembly robot is the assembly of the shaft and the hole. When there is an error in the shaft and the hole, the robot needs to have the flexibility of the movement. Active compliance is to adjust the movement of the robot hand according to the information fed back by the sensor, while the passive compliance center uses an unpowered mechanism to control the movement of the gripper to compensate for its position error.
1. Assembly robots are mainly used in the manufacture of various electrical appliances, (including household appliances, such as televisions, tape recorders, washing machines, etc.) small motors, automobiles and their parts, calculators, toys, assembly of mechanical and electrical products and components, etc.
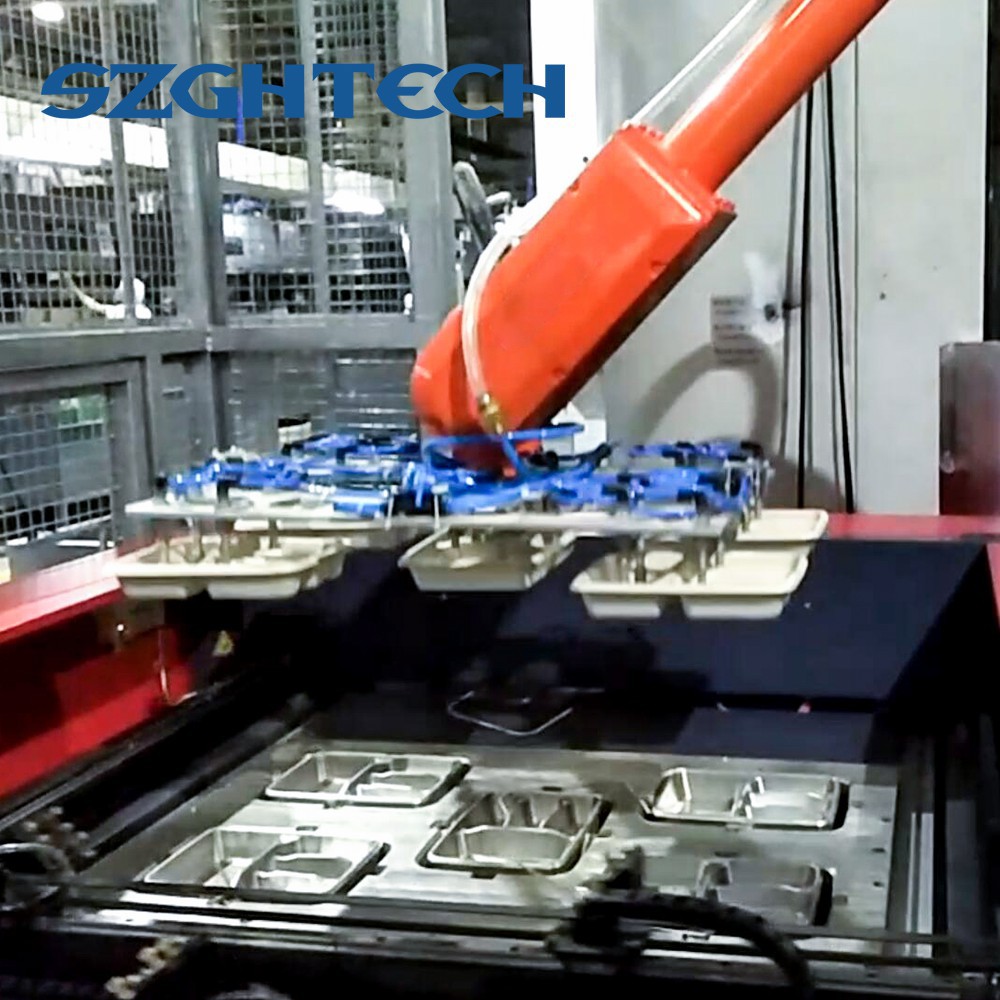
2. The assembly robot is the verification equipment of the flexible automatic assembly system. It is composed of a robot manipulator, a controller, an end effector and a sensor system. The structural types of the robot include horizontal joints, rectangular coordinates, multi-joints and cylindrical coordinates, etc. Generally, multi-CPU or multi-level computer systems are used to realize motion control and motion programming; end effectors are designed into various claws and wrists to adapt to different assembly objects; Information used by objects.
3. Assembly robot features:
1) Each assembly robot arm can be equipped with different tooling according to the process needs to meet the diverse production requirements of multiple batches and small batches in the future production line. It only needs simple programming and tooling replacement to achieve fast switching.
2) The high precision and stability of the robot can be used in the lean industrial production process.
3) The visual function guides the robot to correctly identify and grab the workpiece, and transfer it to the precise assembly position.
4) The input-output ratio of robots is high, and the equipment payback period is short.

